Diagnosis of Celiac Disease
Diagnosis of celiac disease is based on clinical manifestations, blood work, and imaging.
The Gold Standard
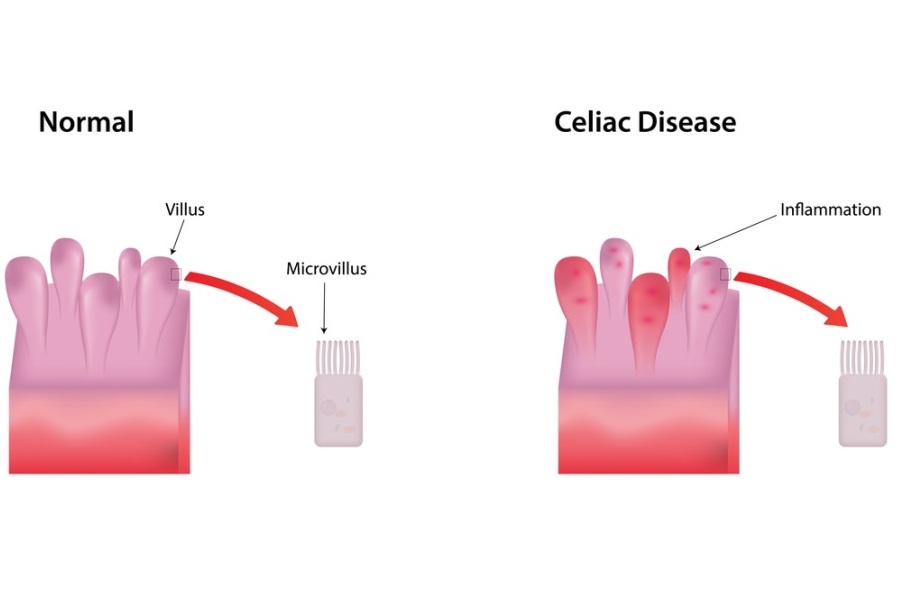
- Histology or biopsy of the proximal small intestinal mucosa is the gold standard for detection of CD. Celiac disease biopsies will show changes in the tissues of gi tract such as mucosal villous atrophy with crypt hyperplasia and/or increased intra-epithelial lymphocytosis.
Blood Tests
- Presence of serum antibodies to deamidated gliadin, endomysium or tissue transglutaminase.
- Anti-tTG antibody: The IgA tTG antibody is the preferred test for screening patients of all ages.
- Anti-deamidated gliadin peptide (DGP) antibody: Immunoglobulin G (IgG)–based DGP antibody is slightly more sensitive than the IgG-based tTG antibody.
- Anti- endomysial antibody: The specificity of these antibodies is higher compared to tTG antibody test.
- Presence of predisposing genetic factors, including human leukocyte antigen markers, HLA DQ2 and HLA DQ8.
- Intraepithelial lymphocytes, mainly for diagnosis of RCD.




